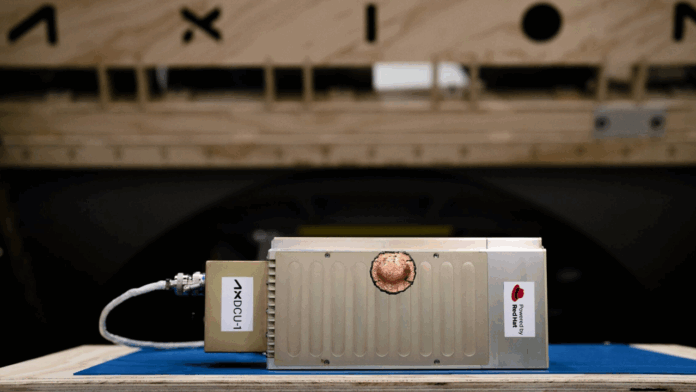
Red Hat, Axiom Space collaborated on a compact edge compute solution, or “orbital data center” for space
A compact prototype for an orbital data center (image above) will soon be on its way to the International Space Station to boost space-based edge computing.
The project, which is scheduled to launch next week on a SpaceX resupply rocket, is a collaboration by Red Hat and Axiom Space, and it’s sponsored by the ISS National Laboratory. The goal is to test the hardware’s ability to provide increased data storage and real-time data processing in space, potentially for everything from monitoring astronauts’ health to supporting microgravity experiments.
The prototype will also serve as a testbed for a future, full Orbital Data Center (ODC) by Axiom, which has laid out a vision for multiple, free-flying data center nodes to operate in low Earth orbit and support government and commercial customers. Axiom has described the ODC project as one that aims to “[enhance] cybersecurity, [reduce] data processing delays, and [support] microgravity research, advanced manufacturing, and in-space data services for satellites and security networks, operating either as an extension of terrestrial cloud systems or independently in orbit.”
“This technology could enable real-time processing of data close to where it is generated, reducing the need for downlink bandwidth, which is precious in space,” said Tony James, chief architect of science and space at Red Hat. “It could also enable time-sensitive decision making and a bit of autonomy. As experiments are running in space and decisions need to be made, you aren’t having to wait hours or days for information from the ground.”
The project is also aimed at figuring out how an orbital data center, or orbital data center nodes, support the compute needs of future commercial space stations. “You need to ensure a space-based software platform has an appropriate level of resistance to damage from harsh conditions and the ability to self-heal with limited or no human intervention,” James said. “The system we are testing addresses those capabilities.”
In other test news:
–Ericsson has received special temporary authority from the Federal Communications Commission to conduct demonstrations of private LTE in Band 26 (862-869 MHz) for utilities at this fall’s Utility Broadband Alliance (UBBA) summit and plugfest in Charlotte, North Carolina. According to a filing with the FCC, Ericsson will be using the temporary access to the spectrum to “support ecosystem testing and demonstrations of utility use case solutions enabled by mission-critical private LTE networks covering a utility grid.
“This work will facilitate the adoption of private LTE for grid modernization, mission critical communications, and AMI 2.0 Smart metering,” the company added.
–O-RAN Alliance is looking for participants for its fall global plugfest, a series of testing events which will be conducted in labs around the world between August and November. More than two dozen operators and independent institutions in 19 labs in different regions around the world will host the plugfest sessions.
This fall’s plugfest will focus on six themes for testing: 1) O-RAN system testing with Layer 1 acceleration, 2) Demonstrating consistent and repeatable open fronthaul testing in multiple labs, 3) O-RAN energy consumption, efficiency and savings, 4) O-RAN end-to-end deployment templates, DevOps, and test automation, 5) the diversity of the O-RAN White-box Hardware ecosystem, and 6) Open fronthaul transport testing with multiple O-RUs.
–Keysight Technologies reported financial results for its fiscal third quarter of the year and raised its outlook for the year.
Keysight delivered revenues of $1.35 billion, compared with $1.22 billion during the same period last year. Net income was down to $191 million from $389 million during the third quarter of fiscal 2024.
Keysight’s Communications Solutions Group (CSG) achieved revenues of $940 million, up 11% from the same time last year. Keysight noted that CSG saw 13% growth in revenues from commercial communications customers.
Meanwhile, the company’s Electronic Industrial Solutions Group (EISG) accounted for $412 million in revenues, an increase of 11% year-on-year driven by growth in the semiconductor, general electronics and automotive and energy sectors.
“Keysight delivered strong results this quarter, exceeding the high end of our guidance for both revenue and earnings per share. We are executing our strategy and capitalizing on the opportunities in our end markets,” said Satish Dhanasekaran, Keysight’s President and CEO. “We are raising our outlook for the full year once again and continue to see solid demand and strong customer engagements.”
-Some new signs of further NTN development: Rohde & Schwarz said that it has verified new test cases for the use of 5G New Radio in Non-Terrestrial Networks. The test company said that it conducted the first test cases of the 3GPP NR-NTN standard with Tier 1 chipset vendors, based on Global Certification Forum and PTCRB’s WI-555 work item and Request for Testing (RFT) 555.
-Meanwhile, Anritsu worked with Microwave Vision Group (MVG) on a joint testing solution for over-the-air (OTA) validation of NTN communications. MVG adapted its multi-probe OTA systems to integrate Anritsu’s Radio Communication Analyzer MT8821C, which the two companies said creates a test environment for “realistic satellite link emulation in compliance with 3GPP requirements.”

“By adapting our test chambers to operate with the MT8821C, we’re giving R&D teams the ability to emulate key NTN communication scenarios directly in the lab,” said MVG’s OTA Product Manager, Sebastien Gaymay. He added that this “enables earlier debugging and faster development cycles for satellite-capable mobile and IoT devices.”