Private 5G spending will hit $5bn by 2028 (41% CAGR), push-to-talk revenues will reach $12bn (11% CAGR), and Industry 4.0 sales will climb to $1.6tn by 2030 (19.4% CAGR) – reflecting rapid digital transformation across sectors.
In sum – what to know:
Private 5G – spending will reach $5bn by 2028 (41% CAGR); China leads deployment scale; spectrum liberalization is driving adoption worldwide.
Push-to-Talk – mission-critical and broadband PTT sales will reach $12bn by 2028 (11% CAGR); adoption across public safety, transport, logistics.
Industry 4.0 – global revenues will hit $1.6tn by 2030 (19.4% CAGR), driven by IIoT, automation, robotics; North America will lead adoption.
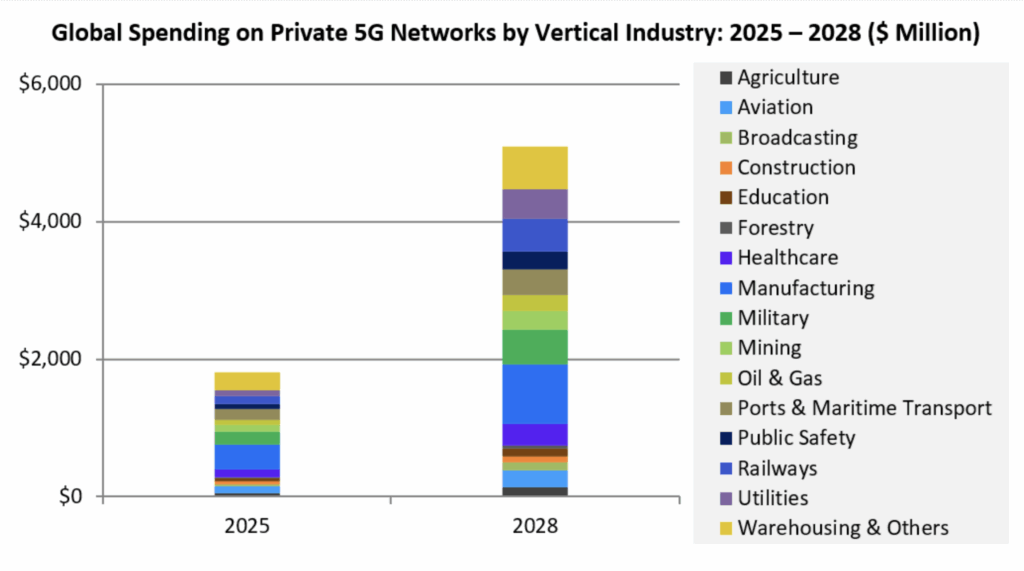
Private 5G networks will account for $5 billion in annual spending by 2028, reckons SNS Telecom & IT. This will be achieved with compound sales growth (CAGR) of 41 percent per annum over the period. They are “on the verge of mainstream adoption”, it says, citing “accelerated investments” by “household names and industrial giants”. The firm has a(nother) new report on the subject, with a hefty promotional extract with long lists about big deployments, global bands, and sundry vendor companies. Most have been written about in these pages. 2025 has been a bonanza year, it writes.
SNS Telecom & IT says: “Private LTE is a well-established market, around for more than a decade, albeit as a niche segment of the wider cellular infrastructure sector… Private [5G is] on the cusp of becoming a mainstream technology, with a market potential exceeding that of private LTE.” It references “production-grade deployments” by Airbus, Aker BP, Boliden, Coal India Limited (CIL), Equinor, Etihad, Ford, Hutchison Ports, Hyundai, Jaguar Land Rover, John Deere, LG Electronics, Lufthansa, Newmont, POSCO, Tesla, Toyota, and Walmart.
RCR may yet copy-and-paste its list of deployments, just to memorialise these “household names and industrial giants”, but SNS Telecom & IT observes “productivity and efficiency gains for specific manufacturing, quality control, and intralogistics processes in the range of 20 to 90 percent”, plus anecdotal reports of labour savings (“55 percent at a warehousing facility”), op-ex savings (“up to 40 percent lower at an intermodal rail terminal”), and fewer worker accidents and harmful gas emissions (“20 percent and 30 percent at an oil refinery”).
It puts some focus on China, as well – as the “most mature national market thanks to state-funded directives aimed at accelerating adoption of 5G in industrial settings”. It says: “As context, the largest private 5G installations in China can comprise hundreds to even thousands of dedicated RAN nodes supported by on-premise or edge cloud-based core network functions depending on specific latency, reliability, and security requirements.” Enterprises State Grid, Midea, and Wanhua Chemical are “among the front-runners” for adoption of reduced capability 5G (5G RedCap).
Recently, Chinese mobile operators and vendors have expanded beyond their domestic market in pursuit of private 5G business abroad – “from Thailand’s manufacturing sector to mining in South Africa,” it says. A chart from the report says manufacturing and warehousing – the distribution and production points in Industry 4.0 – are the top vertical sectors in 2025, and will remain so in 2028; but railways, healthcare, mining, and the military look like significant growth sectors over the next years.
Note to India: SNS Telecom & IT also says spectrum liberalization initiatives – “particularly shared and local spectrum licensing frameworks for mid-band 5G NR frequencies” – have had a “pivotal role” in driving adoption. It lists the work, completed or ongoing, by regulators in the US, Canada, Germany, UK, Ireland, France, Spain, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Poland, Slovenia, Lithuania, Moldova, Bahrain, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Australia, and Brazil.
Mission-crtical PTT
Meanwhile, the same firm has a related forecast about push-to-talk (PTT) subscriptions over commercial operator and critical broadband networks, which will surpass $12 billion by the end of 2028, it reckons. The SNS Telecom & IT review covers mission-critical PTT (MC-PTT), as an evolution of PTT over-cellular (PoC / PTToC) technology, positioned as an upgrade on mission-critical land mobile radio (LMR) systems such as APCO P25 and TETRA. PTT remains a go-to application for private 5G in Industry 4.0, as well – although the report only covers public carrier networks and dedicated critical comms networks for emergency services and specialist industries.
These include: South Korea’s Safe-Net and LTE-R networks; the US’s FirstNet network; the UK’s ESN (Emergency Services Network) setup; France’s RRF (Radio Network of the Future) service; Hub One’s private cellular network in Paris airports; Spain’s SIRDEE (State Emergency Digital Radiocommunications System) network; the Italian Ministry of Interior’s public safety LTE platform; Tampnet’s offshore private 4G/5G networks; Finland’s VIRVE 2.0 broadband service; Türkiye’s KETUM hybrid narrowband-broadband system; Oman’s public safety broadband network; the Qatar Ministry of Interior’s private LTE network; and Nedaa’s 4G network for critical communications in Dubai.
It says MCPTT and broadband PTT service revenues will grow at a CAGR of 11 percent to 2028, reaching $12 billion by the end of the period. Non-critical PTT will constitute the bulk of subscriptions, but most new growth will be driven by higher-end 3GPP offerings, adopted by organizations in various industries. These include the Korean national police and fire agencies (KNPA, NFA), plus “mid-sized and smaller” entities such as the City of Buenos Aires, Amsterdam Schiphol Airport, Rijkswaterstaat, Westphalian State Railway, Société du Grand Paris, Groupe ADP, DHL, plus many state/local first responder agencies in the US.
Industry 4.0, at large
More closely related to the first (private infrastructure) forecast, another analyst firm, BCC Research, has a new Industry 4.0 forecast for the period to 2030, which says sales revenue will top $1.6 trillion by 2030, representing a CAGR of 19.4 percent from $655.2 billion in 2025. The forecast covers global sales of big data and analytics, cloud computing, industrial IoT, augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), robotics, 3D printing, digital twins, system integration, and cybersecurity technologies.
BCC Research sees “rapid growth and integration of advanced Industry 4.0 tech across global industries”. In particular, it cites the expansion of IoT (“transforming industries by connecting machines, systems, and devices to share data seamlessly”) and real-time data (“continuous data streams vital for monitoring, analysis, and optimization”), plus increased government funding for robotics R&D (“to drive innovation, improve productivity, and address demographic challenges”, apparently), and increasing labour shortages (“aging populations and skill gaps”).
A couple of (quoted) facts from the report:
- In 2024, IIoT held the largest market share of 39.3% in the industry 4.0 technologies market. The rapid adoption of IIoT in the manufacturing sector for increased productivity and efficiency, the growing demand for automation across industries, and the use of IIoT for predictive maintenance and data-driven decision making drive demand for IIoT in the Industry 4.0 technologies market.
- The North America region is the largest market, primarily due to its strong industrial base and investments in R&D of technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing. Furthermore, the region’s robust digital infrastructure and major technology corporations such as Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet (Google), and Nvidia, facilitate the widespread adoption and integration of these advanced solutions across various sectors.

