For the test, SoftBank used an Ising machine — a combinatorial optimization quantum system — to recalibrate base station carrier-aggregation settings
In sum – what to know:
Testing quantum – SoftBank is testing the potential of quantum computing to improve RAN performance in 5G networks by recalibrating base station CA settings.
Quantum beyond CA – The operator is also exploring other ways to use quantum computing in broader network architecture and operational scenarios.
SoftBank Corp. has broken new ground in mobile network performance by deploying quantum computing technology in a trial of its 5G Radio Access Network (RAN). In a Tokyo proof-of-concept, the Japanese operator used an Ising machine — a combinatorial optimization quantum system — to recalibrate base station carrier-aggregation (CA) settings, achieving a 10% increase in downlink speeds and up to 50% growth in data transmission capacity.
“These results demonstrate that optimizing base station settings using an Ising machine enables more efficient utilization of the radio spectrum and leads to improved communication performance,” said SoftBank. “This technology contributes to delivering a more seamless user experience, such as smoother high-resolution video streaming and online gaming.”
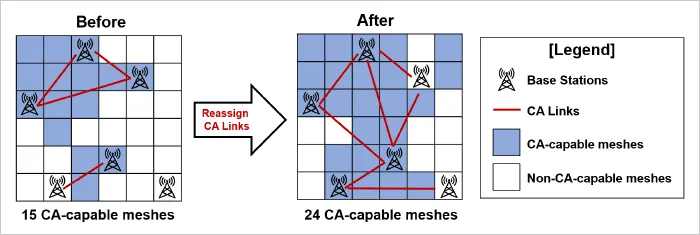
As the number of 5G base stations grows, optimizing CA links becomes exponentially complex — SoftBank cited 35 trillion possible configurations just from ten base stations. “Moreover, constraints such as the maximum number of CA links assignable to each base station further complicate the task, making it extremely difficult to identify the optimal combination that maximizes CA-enabled area coverage,” it added.
In the experiment, SoftBank mapped Tokyo into a granular mesh and applied Ising-augmented optimization to identify the best CA link settings per mesh zone. The outcome: significantly broader CA coverage and more efficient spectrum use.
This isn’t SoftBank’s first quantum plunge. Earlier this year, it announced a quantum collaboration with Quantinuum to build operational use cases and a “quantum data center.” Additionally, it’s advancing AI-RAN infrastructure — through partnerships with Red Hat, Fujitsu, and Nvidia — into a fully orchestrated system known as AITRAS that leverages its AI-RAN orchestrator for dynamic optimization of AI and RAN workloads.
SoftBank plans to expand quantum-based optimization beyond CA into broader network architecture and operational scenarios to build smarter, more adaptive telecom infrastructure and make AI a revenue-generating layer for network operators.