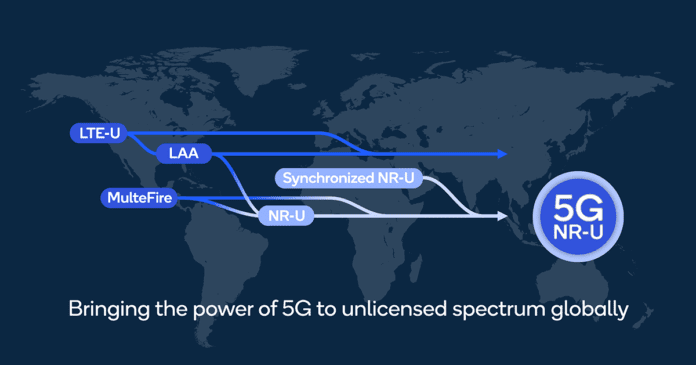
It has been almost a decade since Qualcomm Technologies embarked on the journey to realizing its vision for high-performance cellular networking in unlicensed spectrum. Now, just two years since the launch of 5G NR Release 15, 3GPP is set to complete Release 16 in early July with support for 5G NR operating in unlicensed spectrum or simply, NR-U.
NR-U brings to 5G a variety of options for flexibly utilizing unlicensed spectrum and 3GPP Release 16 is the first global cellular standard that supports both license-assisted and standalone use of unlicensed spectrum. The specifications allow devices to access up to 400 MHz and 100 MHz of unlicensed spectrum bandwidth in the downlink and uplink, respectively.
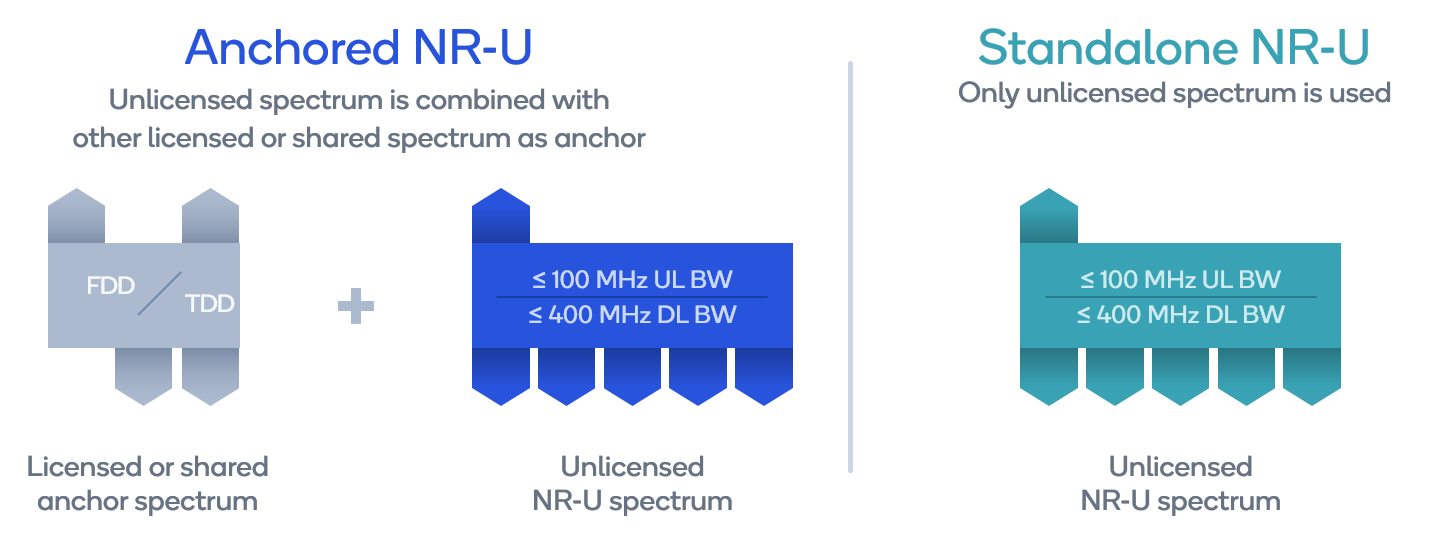
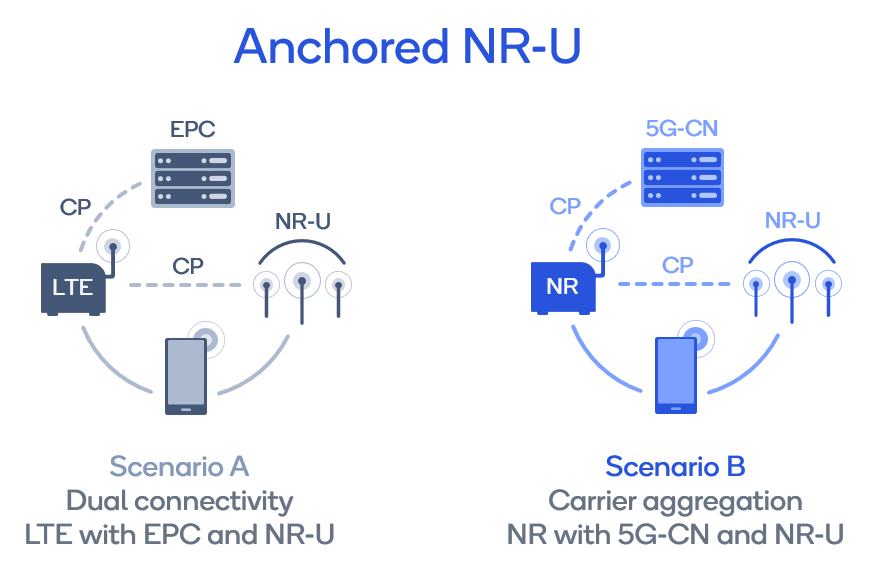
Anchored NR-U
The license-assisted access (LAA) method for accessing unlicensed spectrum, first introduced in 4G as LTE-LAA, will now be supported with 5G NR. This is expected to be useful to mobile network operators (MNOs) as they go beyond delivering their first 5G experiences to addressing the challenges that typically follow, like maintaining the quality of service (QoS) that users would have come to expect by then, despite growth in traffic or subscriber density at hotspots. NR-U can help MNOs address these challenges.

With LAA, a licensed carrier can be thought of as an anchor that stays connected as unlicensed carriers are added to or dropped from the combination of carriers in use between a device and the network. In addition, Release 16 also supports the use of shared spectrum such as the 3.5 GHz Citizens Band Radio Service (CBRS) in the United States as an anchor for unlicensed spectrum with NR-U. Band combinations with CBRS (3GPP Band 48) as the anchor and one or more 5 GHz carriers (3GPP Band 46) have already been included in the standard. This will be useful to multi-service operators (MSOs) and wireless ISPs (WISPs) looking to improve the performance of their CBRS networks.
Continuing with the theme of flexibility, Release 16 has defined two main deployment scenarios for anchored NR-U: dual connectivity for when NR-U works with LTE anchors connected to evolved packet core (EPC) and dual connectivity or carrier aggregation for when NR-U works with NR anchors connected to 5G core network (5G-CN).
Standalone NR-U
NR-U heralds a milestone in cellular communications by being the first global cellular standard to not require licensed spectrum at all for a standalone mode of operation. NR-U offers mobility and the QoS that users have come to expect from 5G NR. This revolutionary capability will extend the power of high-performance 5G to unlicensed spectrum and unlock new opportunities for the industrial Internet of things (IIoT).
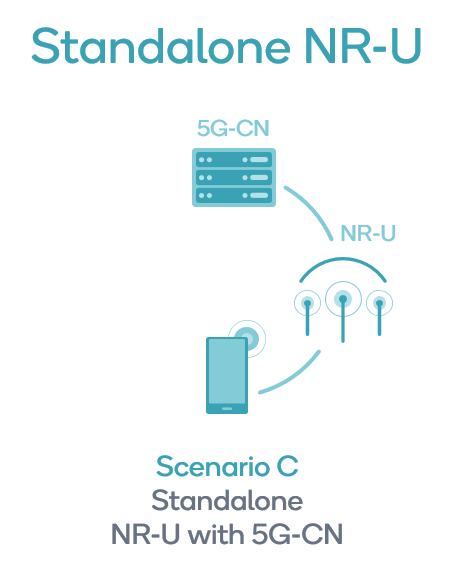
Release 16 has one scenario for NR-U working standalone, without any anchor in licensed or shared spectrum, when connected to 5G-CN. Standalone NR-U has been designed from the ground up to coexist fairly with other unlicensed technologies such as Wi-Fi and LTE-LAA. With core networks becoming easier to manage, NR-U is not only well-positioned to offer simple installation procedures that Wi-Fi is appreciated for but also easily scalable network capacity. NR-U enables support of neutral host networks and mobility offload use cases. These strengths combine to make 5G private networks easy to deploy.

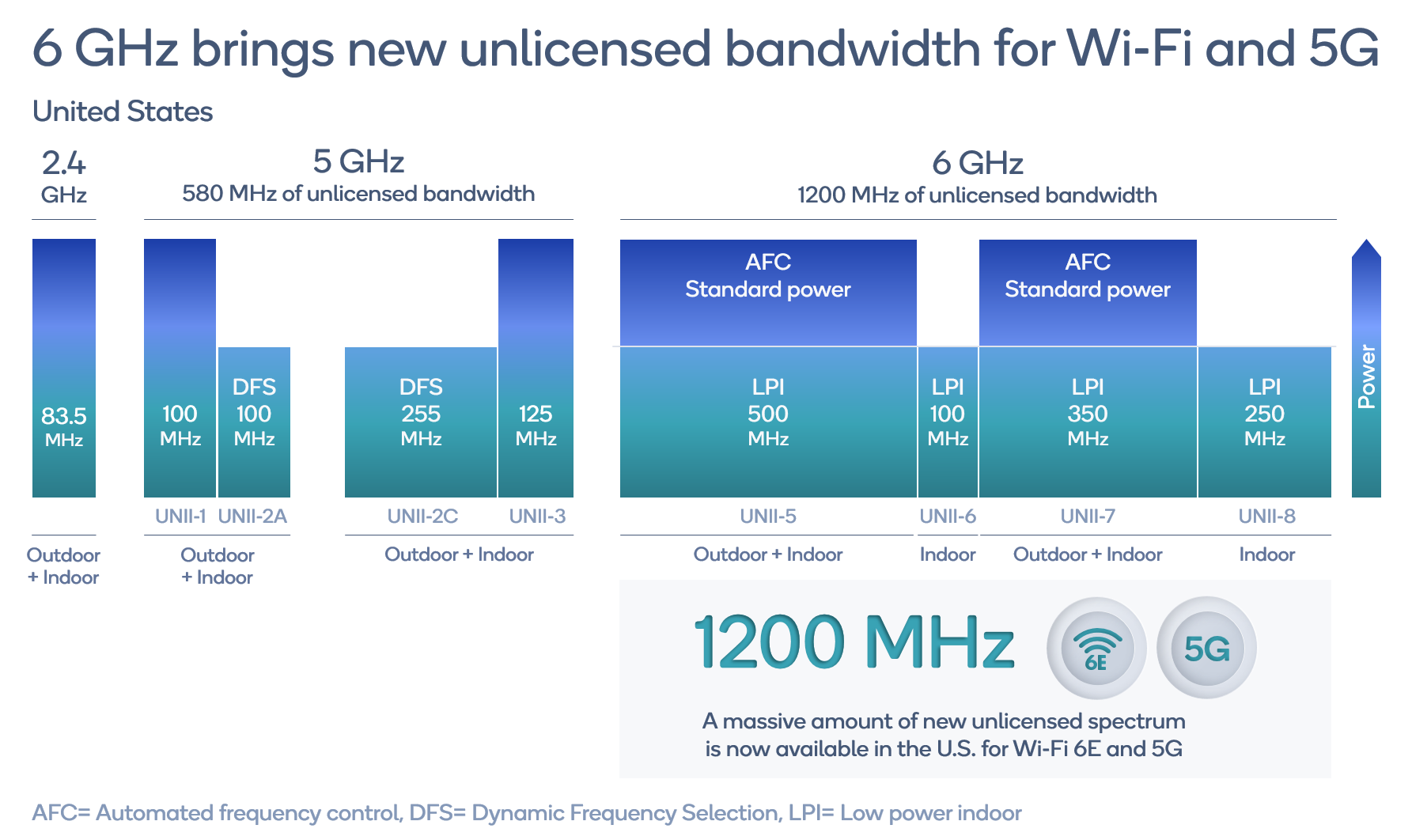
6 GHz greenfield spectrum
Release 16 will have NR-U ready to go on unlicensed 5 GHz bands. 6 GHz unlicensed spectrum is very exciting not only for the new bandwidth it brings but also the flexible ways it may be used in indoor and outdoor environments. 6 GHz would offer greenfield spectrum in indoor environments with natural isolation from the outdoor uses of this band which include incumbent operations. In the United States, the FCC has just recently made a massive 1200 MHz of bandwidth available in this band for Wi-Fi and other unlicensed technologies such as 5G NR-U. We are excited about how 6 GHz could transform what we can achieve with unlicensed spectrum.
Unlicensed spectrum can support demanding IIoT
Many industrial use-cases are critically dependent on time-sensitive networking (TSN) for the deterministic latency it offers. 5G offers a standardized solution to transparently connect existing TSN networks. Other 5G enablers for IIoT such as synchronized sharing, multiple transmission and reception points (multi-TRP) with coordinated multi-point transmissions (CoMP), and enhanced ultra-reliable low-latency communications (eURLLC) can all be deployed with NR-U in controlled environments. NR-U in 6 GHz can also be expected to play a major role for IIoT due to the wide bandwidth the new 6 GHz unlicensed bands have to offer. Reliable 5G wireless connectivity then stands to unlock the hallmark capabilities of Industry 4.0 such as workflow flexibility, machine mobility and operational agility.

Synchronized sharing
Synchronized sharing is a revolutionary capability which unlocks some of the best 5G capabilities for unlicensed spectrum. NR-U with synchronized sharing offers many benefits, including reduced access latency and improved fairness, to all access technologies using the same spectrum. With synchronized sharing in operation, CoMP can then be used to improve either spectral efficiency or reliability. CoMP schedulers can adapt dynamically between the extremes of maximum spectral efficiency and maximum reliability from one scheduling period to the next, depending on the specific QoS requirements of the applications with data in transmission buffers. One NR-U network can then be used to serve diverse applications such as mission-critical sensing and control, video surveillance, augmented or virtual reality (XR) and voice, each of which have different requirements for throughput, latency, jitter and packet loss or reliability.
Summary
NR-U makes advanced features of 5G NR available to unlicensed spectrum globally, including new 6 GHz greenfield spectrum. When combined with licensed or shared spectrum, anchored NR-U helps MNOs deliver 5G with better performance by alleviating spectrum constraints. Standalone NR-U extends the power of high-performance 5G to private networks without requiring any licensed spectrum. In controlled environments, NR-U with synchronized sharing unlocks some of the best 5G capabilities for unlicensed spectrum to support the demanding requirements of IIoT.