AI is driving data center interconnect growth
The AI era is unleashing a new wave of data center interconnect growth. At a recent industry conference, a leading hyperscale operator revealed a striking internal metric: AI-related backbone traffic is growing at an astonishing 100% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). While projections vary among analysts and research firms, the consensus is clear: AI is reshaping infrastructure demands.
The future points to a surge in new data centers, escalating capacity requirements, and a growing need for low-latency, resilient connectivity to support increasingly distributed AI workloads. A recent Bell Labs Consulting study reinforces this trend, showing non-AI traffic growing at a CAGR of approximately 15%, while AI traffic — spanning both enterprise and consumer use cases — is accelerating at over 50% CAGR. These trends are unlocking new opportunities for network operators to leverage optical network infrastructure and deliver wavelength services optimized for the AI era.
All this traffic growth, non-AI, AI indirect and AI direct, combined with the increase in data centers, is driving data center interconnect growth, both the number of interconnects and their speed. 10G client services are being migrated onto 100G wavelength services, while 100G wavelength services are transitioning to 400G, and 400G wavelength services are moving to 800G. This aligns with the rapid adoption of 400GbE within data centers and on router ports, with 800G wavelength services corresponding to the availability and uptake of 800GbE router ports.
What is a wavelength service?
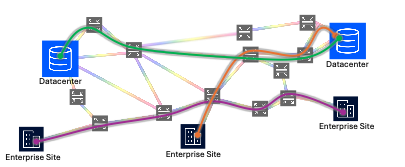
For this article, we define any optical service at 100 Gb/s and above as a wavelength service. Such wavelengths are typically used to connect one data center to another, a key enterprise site to a data center, or, less commonly, one enterprise site to another, as shown in Figure 1. These services are typically delivered by a transponder or muxponder, which generates a high-speed coherent wavelength transported over a WDM optical line system.
These optical line systems usually comprise remote optical add-drop multiplexers (ROADMs) and in-line amplifiers, or, in simpler cases, fixed point-to-point WDM. In addition, optical equipment vendors and service providers have collaborated on Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF — now Mplify Alliance) standards for 100 Gb/s wavelength services for both retail (MEF 63) and wholesale (MEF 64) customers.
Wavelength service attributes: Purchasing criteria and vendor differentiators
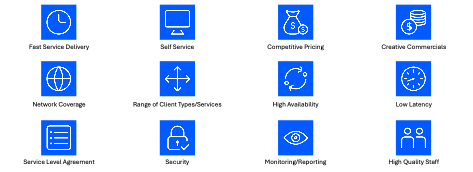
As Figure 2 illustrates, beyond service speed, these services include a wide range of attributes that influence customer vendor selections and help wavelength service providers differentiate themselves, including:
- Fast service delivery: The time from order to service activation is important, as customers often need the service as soon as possible or by a strict deadline.
- Self-service: Some wavelength service providers offer customers the ability to provision, upgrade and downgrade wavelength services remotely from a customer service portal.
- Competitive pricing: While pricing is always important, scaling inter- and intra-data center connectivity requires more than competitive costs. Vendors must deliver the lowest cost per bit and power per bit, while also providing the flexibility needed for AI-driven infrastructure.
- Creative commercials: Beyond price, some vendors differentiate themselves with creative and flexible commercial terms and conditions, including pay-as-you-grow pricing.
- Network coverage: The breadth of geographic network coverage and how this aligns with customer locations is key.
- Range of client types/services: Service speeds range from 10 Gb/s to 800 Gb/s and support multiple protocols, including Ethernet, OTN, and Fibre Channel.
- High availability: Wavelength service vendors often offer both unprotected and protected services. Target availability can be as high as 99.999%.
- Low latency: Latency is typically dominated by the length of the fiber route. Wavelength service providers differentiate on latency by offering the shortest fiber route.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): SLAs can cover a wide range of parameters and targets, with both commercial and non-commercial penalties.
- Security: Some wavelength vendors offer value-added security features, including wire-speed layer 1 encryption. Quantum-safe provides scope for further differentiation.
- Monitoring and reporting: Some wavelength service providers offer the ability to monitor the wavelength service’s performance in real-time from a customer portal.
- High-quality staff: Some wavelength services providers differentiate themselves with their experienced and dedicated staff.
These attributes give wavelength service providers opportunities to differentiate and compete successfully in the growing wavelength services market.
How optical equipment vendors can help
What are vendors doing to help their customers be successful when offering wavelength services? To meet the demand for higher service speeds and lower costs that enable competitive pricing, equipment vendors are advancing their coherent optical engines to support higher baud rates and coherent pluggables. To enable faster service delivery, innovations such as expanding the C+L band (doubling available spectrum from 4.8 THz to 9.6 THz), extending the C-band to Super-C (6.1 THz), and using automation tools to defragment spectrum are all increasing the likelihood that end-to-end spectrum will be available for service delivery.
Other tools to speed service delivery include integrated service testing, zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) and real-time planning and provisioning. Advanced transport controller capabilities and open APIs, such as the Linux Foundation’s T-API, combined with pre-deployed hardware, have enabled one North American operator to offer 24-hour, on-demand wavelength services. To support high availability and strong SLAs, operators are using tools such as 100G+ network demarcation devices, integrated OTDR for rapid fiber-cut localization, optical protection and fast restoration. Security is also becoming a differentiator, with options including wavelength encryption, quantum-safe key exchange and certifications such as FIPS and NIAP.
As AI continues to drive explosive growth in data center interconnect demand, wavelength services represent a compelling and potentially lucrative opportunity for network operators. Beyond competing on price, operators can differentiate by delivering high-performance, scalable solutions tailored to the demands of the AI era.

